In a groundbreaking study, scientists at UT Austin have successfully decoded brain activity into dialogue using artificial intelligence. By creating a 3D view of a person’s brain and analyzing brain scans, the AI was able to translate the brain waves into English and turn it into what appears to be inner dialogue. This leap forward in technology expands upon previous studies that only focused on single words or short sentences, as now researchers can decipher whole strings of text and complex ideas. The potential applications of this technology range from helping stroke victims communicate to everyday use by individuals, but concerns about mental privacy and freedom of thought also arise. This study is a testament to the immense promise of AI technology in understanding the human brain and highlights the need for careful consideration of the ethical implications it presents.
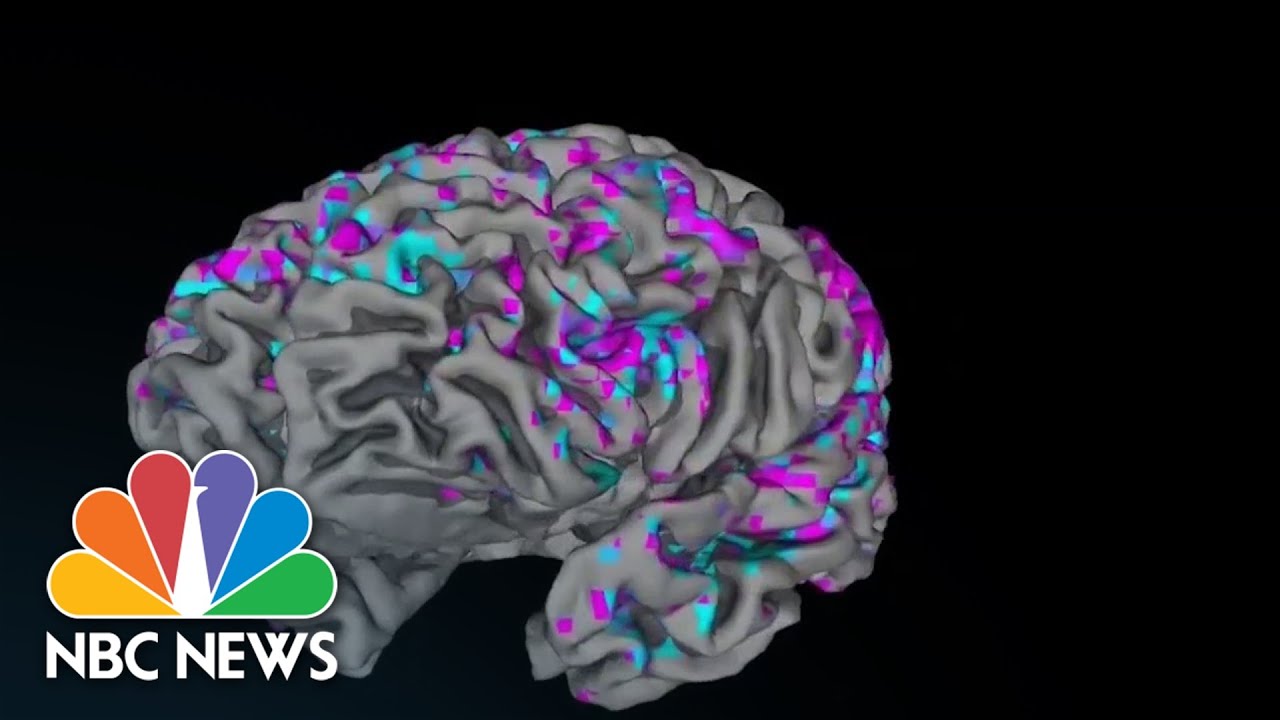
Scientists at UT Austin Study Brain Activity with AI
Scientists at the University of Texas at Austin have conducted groundbreaking research that combines artificial intelligence (AI) and neuroscience. Their study aims to decode brain activity into dialogue by creating a 3D view of the brain and translating brain scans into text through the use of AI algorithms. This research has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the human brain and its functions.
Creating a 3D View of the Brain
The first step in this study involved creating a three-dimensional view of the brain. Scientists at UT Austin used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to track blood flow changes in the brain. This allowed them to visualize regions of above-average and below-average brain activity. By mapping brain activity in this way, researchers gained crucial insights into how different areas of the brain work together and how they contribute to complex cognitive processes.
Decoding Brain Activity into Dialogue
Once the 3D view of the brain was established, the researchers used AI algorithms to decode brain activity into dialogue. By analyzing brain waves and patterns, the AI was able to translate the neural signals into meaningful text. This breakthrough is a significant advancement compared to previous studies, which focused on single words or phrases. With the ability to generate whole strings of text, researchers can now gain even deeper insights into the inner workings of the human mind.
AI’s Ability to Translate Brain Scans into Text
The AI used in this study demonstrated remarkable precision in translating brain scans into text. Volunteers were asked to watch a movie clip without audio, and the AI accurately described the visual stimuli based solely on the brain activity it observed. For example, the AI was able to generate a description like, “I see a girl that looks just like me get hit on her back, and then she is knocked off.” This level of detail and context in translating brain activity opens up new possibilities for understanding complex cognitive processes and even internal dialogue.
Understanding the Potential Impact
The research conducted by scientists at UT Austin has several potential applications that could significantly impact different aspects of society and healthcare.
Applications in Stroke Recovery
One potential application of this research is in stroke recovery. By decoding brain activity into dialogue, individuals who have been affected by strokes or other neurological conditions could regain their ability to communicate. This technology offers the possibility of interpreting a person’s thoughts and translating them into speech or written language, providing a means of communication for those who have lost the ability to speak.
Communication for Individuals with Locked-In Syndrome
Locked-In Syndrome is a condition where a person is fully conscious but unable to move or communicate verbally due to complete paralysis. With the ability to decode brain activity into dialogue, individuals with Locked-In Syndrome could potentially communicate their thoughts and needs to caregivers and loved ones. This would greatly improve their quality of life and provide a sense of agency and independence.
Privacy Concerns and Freedom of Thought
While the potential benefits of this research are significant, it also raises concerns about privacy and freedom of thought. As the technology advances, there is a potential for mental privacy to be compromised. The ability to read and interpret thoughts and brain activity opens up ethical questions about the boundaries between personal privacy and the intrusion of technology. It is crucial to establish guidelines and regulations to protect individuals’ privacy and ensure that the use of this technology is ethical and respects individual human rights.
The Research Process and Findings
The research process involved conducting experiments where volunteers watched movie clips without audio while their brain activity was monitored. By comparing the observed brain activity to the dialogue generated by the AI, researchers were able to validate the accuracy of the AI algorithm in translating brain scans into text.
Viewing Movie Clips Without Audio
Volunteers were asked to watch movie clips without any audio cues. This allowed researchers to observe the brain’s response to visual stimuli and analyze the corresponding patterns of brain activity. This method ensured that the brain’s response was solely based on visual processing and not influenced by other auditory factors.
AI’s Description of Brain Activity
The AI algorithm used in the study accurately described the brain activity of the volunteers based on the observed fMRI data. The AI-generated text provided detailed descriptions of the visual stimuli, showcasing its ability to interpret and translate brain activity into coherent dialogue.
Implications for Mental Privacy
The success of this research raises concerns about mental privacy. As technology advances, the ability to read and interpret thoughts and brain activity may become more accessible. Therefore, it is important to address the ethical implications and establish safeguards to protect individuals’ privacy rights and prevent any potential misuse of this technology.
Testing with Portable Devices
In addition to the initial research, scientists at UT Austin explored the potential for using portable devices to achieve similar results.
Using Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy
To test the feasibility of portable devices, the researchers used functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). This wearable device measures changes in oxygen levels in the brain, providing insights into brain activity. By using fNIRS, the scientists aimed to replicate the accuracy of the AI algorithm in a more accessible and portable format.
Achieving Precision with Portable Devices
The results of the study using fNIRS were promising. The researchers found that the same level of precision could be achieved with portable devices compared to the traditional fMRI machines. This suggests that everyday mind reading may become a reality, with individuals using wearable devices to track their brain health and gain insights into their cognitive processes.
Possibility of Everyday Mind Reading
The potential for everyday mind reading raises concerns about privacy and data ownership. As companies like Meta and Snapchat develop their own neurotechnology and incorporate brain activity sensors into everyday devices, individuals’ thoughts and brain activity could become accessible to external entities. Protecting personal data and ensuring privacy rights will be crucial in this evolving landscape.

The Role of AI and Neurotechnology
AI plays a crucial role in the field of neurotechnology. It enables the translation of complex brain activity into meaningful dialogue and provides insights into the inner workings of the human mind.
AI’s Role in Mind Reading
AI algorithms, such as the one used in the UT Austin study, have the ability to decode brain activity and translate it into text. By analyzing patterns and signals in the brain, AI can generate meaningful dialogue that represents an individual’s thoughts and inner dialogue.
Concerns about Infringement on Mental Privacy
The advancement of AI and neurotechnology raises concerns about infringement on mental privacy. As technology progresses, the accessibility and accuracy of mind reading algorithms could lead to potential misuse. Safeguarding mental privacy and establishing regulations that protect individuals’ thoughts and brain activity will be essential.
Potential for Manipulation and Interference
As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, there is a potential for manipulation and interference. By understanding an individual’s thoughts and brain activity, external entities may be able to influence their thinking or behavior. This possibility raises ethical questions and emphasizes the need for responsible development and regulation of AI in neuroscience.
Corporate Ownership and Brain Wearables
The development and integration of neurotechnology into everyday devices by corporations like Meta and Snapchat has significant implications for privacy and individual rights.
Meta and Snap’s Neurotechnology Developments
Companies like Meta and Snapchat are investing in neurotechnology and developing devices that incorporate brain activity sensors. These devices, such as earbuds or headphones, have the potential to track brain activity while individuals engage in everyday activities like taking a conference call or listening to music. The integration of neurotechnology into these devices opens up new possibilities but also raises concerns about data ownership and privacy.
Adding Brain Activity Sensors to Everyday Devices
The inclusion of brain activity sensors in everyday devices has both benefits and risks. On one hand, it allows individuals to track their brain health and gain insights into their cognitive processes. On the other hand, it raises concerns about the collection and use of personal data, as companies may have access to intimate details of an individual’s thoughts and emotions.
Access to Personal Data and Brain Activity
The integration of brain activity sensors into everyday devices gives corporations access to personal data related to thoughts and brain activity. This raises significant privacy concerns and highlights the need for individuals to have control over their own data. Transparent data policies and regulations are essential to protect individuals’ privacy rights in this evolving landscape.

Implications for Privacy Rights
The research conducted by scientists at UT Austin carries implications for privacy rights, freedom of thought, and the influence of technology on individuals’ lives.
Concerns about Mental Privacy
As technology progresses, the ability to read and interpret thoughts and brain activity raises concerns about mental privacy. The intimate details of an individual’s thoughts and inner dialogue may become accessible to external entities, leading to potential infringements on privacy rights. Safeguarding mental privacy will be crucial in an increasingly technologically connected world.
Freedom of Thought and Individual Rights
Protecting freedom of thought is paramount in any discussion surrounding brain activity decoding and the use of AI algorithms. Individuals must maintain the right to privacy and autonomy over their own thoughts. Balancing the potential benefits of AI in neuroscience with the preservation of individual rights will be a key challenge moving forward.
Interference with Social Media Algorithms
The information gleaned from decoding brain activity has the potential to interfere with social media algorithms and personalized content delivery. By understanding an individual’s thoughts and preferences, external entities may be able to manipulate the information individuals receive through their online platforms. This interference raises concerns about the impact on individual autonomy and the need for transparent and ethical algorithms.
Future Challenges and Unforeseen Consequences
As AI and neuroscience continue to advance, future challenges and unforeseen consequences are likely to emerge. Preparing for an unanticipated future requires careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits associated with these technological advancements.
Preparation for an Unanticipated Future
The rapid pace of technological advancement demands proactive measures to anticipate and address future challenges. Researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders must work together to establish guidelines, regulations, and ethical frameworks to shape the responsible development and use of AI in neuroscience.
Potential Need for Legislative Measures
The complex nature of AI and neuroscience necessitates legislative measures to ensure the protection of privacy rights and individual freedoms. The government and regulatory bodies need to stay informed about the latest advancements and engage in ongoing dialogue and collaboration with researchers and industry experts.
Balancing Technological Advancements with Privacy Rights
Striking a balance between technological advancements and privacy rights is a crucial challenge. It will require careful consideration of the potential risks and ethical implications associated with the use of AI in neuroscience. By prioritizing privacy and individual rights, society can harness the benefits of AI while minimizing potential harm.

The Promise and Risks of AI in Neuroscience
The field of AI in neuroscience holds vast promise for advancements in healthcare and our understanding of the human mind. However, it also brings ethical implications and potential dangers that must be carefully navigated.
Promising Applications in Healthcare
The research conducted by scientists at UT Austin has promising applications in healthcare. The ability to decode brain activity into dialogue can help individuals with conditions like stroke or Locked-In Syndrome communicate their thoughts and needs. It also has the potential to enhance brain health monitoring and aid in early detection and treatment of neurological disorders.
Ethical Implications and Dangers
Despite the potential benefits, the field of AI in neuroscience raises important ethical questions and potential dangers. Protecting mental privacy, preserving freedom of thought, and ensuring responsible use of the technology are crucial. Ethical frameworks and regulations must be established to guide the development and adoption of AI in neuroscience.
Continued Dialogue and Research
As AI and neuroscience continue to advance, continued dialogue and research are essential. Collaboration between scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public is crucial in shaping the future of AI in neuroscience. Open and inclusive discussions are necessary to address ethical concerns, mitigate risks, and maximize the benefits of this technology.
Conclusion
The research conducted by scientists at the University of Texas at Austin represents a significant advancement in the field of AI and neuroscience. By decoding brain activity into dialogue, researchers have opened up new possibilities for understanding the human mind and potential applications in healthcare. However, this research also raises important ethical questions regarding privacy, mental autonomy, and the responsible use of technology. As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of AI in neuroscience, it is crucial to prioritize individual rights, establish clear guidelines, and maintain an ongoing dialogue to ensure the ethical and responsible development and deployment of these technologies.






Leave a Reply